Azure
Prerequisites (~30-60 minutes)
- Have an active Azure account. If you don’t have one yet, they give you $200 worth of credit to use within the first 30 days!
- Install Terraform and move it to a directory included in your system’s PATH.
- Install Ansible. This will be used to provision the instances. Some users may prefer to install Ansible inside of a virtual environment; that’s fine too.
- Install the Azure command line client and make sure it’s included in your system’s PATH.
- Either create or re-use an existing SSH keypair that you’ll use to authenticate to the logger host
- Make sure you’ve pulled down the most recent changes from the DetectionLab git repo
- Please note that the default credentials before provisioning are
vagrant:Vagrant123due to the windows SKU/AMI password complexity requirements!
Steps
Terraform
-
(5 Minutes) - Configure the
terraform.tfvarsfile- Copy the file at
DetectionLab/Azure/Terraform/terraform.tfvars.exampletoDetectionLab/Azure/Terraform/terraform.tfvars - In the newly copied terraform.tfvars, provide a value for each variable.
Failing to complete this step will cause the lab to be unreachable.
- Copy the file at
-
(5 Minutes) - Authenticate to Azure using
az- Run
az login. This should bring up a browser that asks you to sign into your Azure account. - Sign in and the window should say “You have logged into Microsoft Azure!”
- Run
-
(3-20 Minutes) - Bring up the VM’s using Terraform
cdtoAzure/Terraformand runterraform initto initialize the working directory- Make sure you followed the pre-reqs and have a
terraform.tfvarsfile present with your public IP address whitelisted - Run
terraform applyto check the Terraform plan orterraform apply --auto-approveto bypass the check - It will take ~20 minutes for logger to come online and finish provisioning, but you can move onto the next step once you see that DC, WEF, and WIN10 have fininshed creation (usually around 2 minutes):
azurerm_virtual_machine.dc: Creation complete after 1m55s azurerm_virtual_machine.wef: Creation complete after 1m54s azurerm_virtual_machine.win10: Creation complete after 1m55s
At this point in time, we’re at this state:
- Logger VM has been brought up and is provisioning
- DC VM has been brought up but is unprovisioned
- WEF VM has been brought up but is unprovisioned
- WIN10 VM has been brought up but is unprovisioned
At this point in time, you should be able to open a new terminal window, navigate to DetectionLab/Azure/Terraform and run terraform output. You should see something like the following:
dc_public_ip = 52.183.119.x
fleet_url = https://52.191.170.x:8412
guacamole_url = https://52.191.136.x:8080/guacamole
logger_public_ip = 52.191.170.x
region = West US 2
splunk_url = https://52.191.170.x:8000
wef_public_ip = 52.191.136.x
win10_public_ip = 52.229.34.x
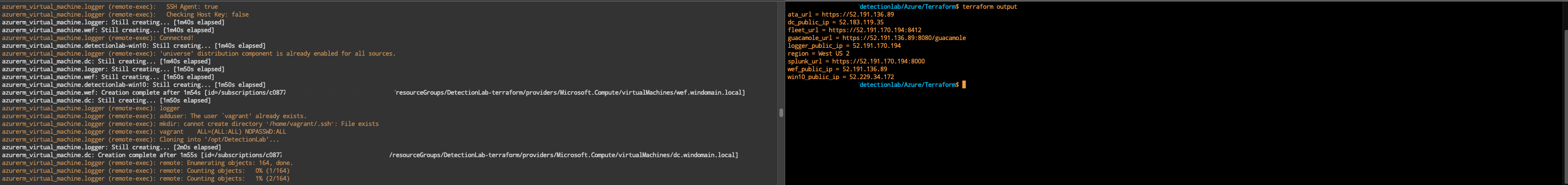
We’re going to use this output in the next step.
Ansible
We’re going to use Ansible to fininsh provisioning the rest of the Windows hosts.
- (5 Minutes) - Configure the
inventory.ymlfile- Navigate to
Azure/Ansibleand openinventory.ymlfor editing. - Take the
public_ipvalues fromterraform outputand replace thex.x.x.xvalues with the public IP of each hostNOTE: I’ve added a script at
DetectionLab/Azure/build_ansible_inventory.shto help automate this for MacOS and Linux users.
- Navigate to
Now that Ansible is configured for provisioning, there are two ways to go about this:
- Provision each host one at a time (e.g. DC, then WEF, then WIN10). This is slower, but requires less steps.
- Provision the DC, then provision WEF and WIN10 simultaneously. This is faster, but you’ll have to open multiple terminals and do a bit of manual work.
For the provisioning to be successful, the DC has to spin up Active Directory before provisioning of the WEF and WIN10 hosts can begin, otherwise they will fail to join the domain and provisioning will fail.
Slow but steady
If you’d like to take the slower but easier route, ensure you’re in the DetectionLab/Azure/Ansible directory and run ansible-playbook -v detectionlab.yml. This will provision the hosts one at a time (DC, WEF, then WIN10). However, if you’d like to go the faster route, follow the directions below.
Faster, but more hands-on
If you’d like to take the faster route, I recommend opening 3 terminal windows to DetectionLab/Azure/Ansible and following these steps:
- In the first window, run
ansible-playbook -v detectionlab.yml --tags "dc" - Once the DC has passed the
Reboot Afer Domain CreationAnsible step, you can begin provisioning WEF and WIN10 - In the second window, run
ansible-playbook -v detectionlab.yml --tags "wef" - In the third window, run
ansible-playbook -v detectionlab.yml --tags "win10"
If you run into any issues along the way, please open an issue on Github and I’ll do my best to find a solution.
Debugging / Troubleshooting / Known Issues
- If an Ansible playbook fails (and they sometimes do), you can pick up where it left off with
ansible-playbook -vvv detectionlab.yml --tags="hostname-goes-here" --start-at-task="taskname" - “Installing Red Team Tooling” hangs if AV isn’t disabled successfully
Future work required
- I imagine there’s a streamlined way to get the results of
terraform outputinto theinventory.ymlfor Ansible. - I’m guessing there’s a way to parallelize some of this execution or make some of it asynchronous: https://medium.com/developer-space/parallel-playbook-execution-in-ansible-30799ccda4e0 and https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/playbooks_async.html
Credits
As usual, this work is based off the heavy lifting that others have done. My primary sources for this work were:
- The DetectionLab work that juju4 has been doing on Azure and Ansible. At least 90% of this code was borrowed from their work.
- Automate Windows VM Creation and Configuration in vSphere Using Packer, Terraform and Ansible - Dmitry Teslya
Thank you to all of the sponsors who made this possible!